step 1
더보기
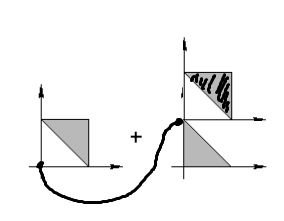
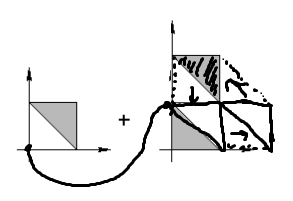
다각형 A의 원점을 다각형 B의 한 꼭짓점으로 이동시켜 봅시다. 그때, 다각형 A가 차지하는 영역은 민코프스키 합에 포함됩니다.

이제 A의 원점을 B의 테두리를 따라 이동시킨다고 생각해 봅시다. 그때 A가 지나는 모든 영역은 민코프스키 합에 포함됩니다. 그리고 그 내부 역시 민코프스키 합에 포함됩니다.

다각형 A, B 둘 다 볼록다각형 1개로 이루어져 있으므로 이렇게 만들어진 영역 역시 볼록다각형입니다.
step 2
더보기
모든 A의 꼭짓점 $(a_x, a_y)$과 모든 B의 꼭짓점 $(b_x,b_y)$에 대해 $(a_x+b_x, a_y+b_y)$를 계산합니다. 각 다각형은 최대 1000개의 꼭짓점을 가지므로 총 1,000,000개의 꼭짓점이 나옵니다.
이 꼭짓점을 모두 포함하는 볼록다각형을 구하면 해결할 수 있습니다.
코드
더보기
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct dataa {
long long int x, y;
inline bool operator<(const dataa& temp)const {
return x<temp.x || x==temp.x && y<temp.y;
}
}b1[2000],b2[2000],b[1000010],s1[1000100], s2[1000100];
long long int sc1, sc2;
long long int ccw(dataa x,dataa y,dataa z) {
if (x.x * y.y + y.x * z.y + z.x * x.y - (x.y * y.x + y.y * z.x + z.y * x.x) < 0) return -1;
if (x.x * y.y + y.x * z.y + z.x * x.y - (x.y * y.x + y.y * z.x + z.y * x.x) > 0) return 1;
return 0;
}
int main() {
long long int n, m, i, j;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
for (i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
scanf("%lld%lld", &b1[i].x, &b1[i].y);
}
long long int cnt = 0;
for (i = 1;i <= m;i++) {
scanf("%lld%lld", &b2[i].x, &b2[i].y);
for (j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
cnt++;
b[cnt].x = b1[j].x + b2[i].x;
b[cnt].y = b1[j].y + b2[i].y;
}
}
sort(b + 1, b + cnt + 1);
for (i = 1;i <= cnt;i++) {
while (1) {
if (sc1 < 2) {
sc1++;
s1[sc1] = b[i];
break;
}
if (ccw(s1[sc1 - 1], s1[sc1], b[i]) <= 0) { sc1--; continue; }
sc1++;
s1[sc1] = b[i];
break;
}
}
for (i = 1;i <= cnt;i++) {
while (1) {
if (sc2 < 2) {
sc2++;
s2[sc2] = b[i];
break;
}
if (ccw(s2[sc2 - 1], s2[sc2], b[i]) >= 0) { sc2--; continue; }
sc2++;
s2[sc2] = b[i];
break;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", sc1 + sc2 - 2);
for (i = 1;i <= sc1;i++) {
printf("%lld %lld\n", s1[i].x, s1[i].y);
}
for (i = sc2-1;i >= 2;i--) {
printf("%lld %lld\n", s2[i].x, s2[i].y);
}
return 0;
}'PS - 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 29845 - Pipes (0) | 2025.02.10 |
|---|---|
| 20121 - 카드 셔플 (0) | 2025.01.13 |
| 10919 - 선물상자 (0) | 2024.12.30 |
| 18407 - 가로 블록 쌓기 (1) | 2024.12.23 |
| 2834 - 박스 정렬 (0) | 2024.12.16 |

